- About Us
-
Products & Services
Customize me!
Leam more about Naturalin Agricultural
Custom solutions. MORE +
- Quality
- Sustainability
- News
- Contact Us
How to distinguish Cordyceps Militaris and Cordyceps Sinensis?
Post time: 2025-12-31
Cordyceps Militaris and Cordyceps Sinensis, with their similar-sounding names and reputations as nutrient-dense natural products, are frequently conflated in the market and among consumers. Both have carved out significant niches in the fields of health preservation, functional food, and cosmeceuticals due to their rich biological active ingredients. However, they differ fundamentally in terms of biological nature, growth patterns, morphological characteristics, and practical applications. Clarifying these differences is not only crucial for consumers to make informed purchasing decisions but also essential for industry professionals to ensure accurate product development and marketing.

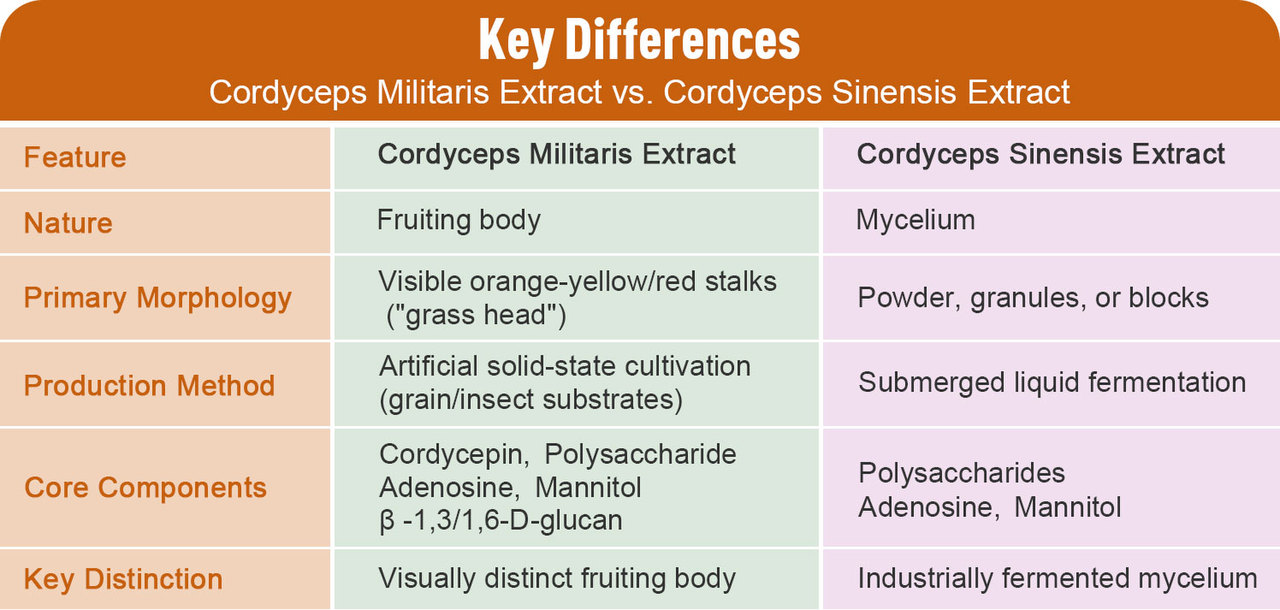
Cordyceps Militaris: The Cultivated Fruiting Body with Distinctive Morphology
Cordyceps Militaris, scientifically named Cordyceps militaris, goes by various common names such as Northern Chinese Cordyceps, Bei Chong Cao, Cultivated Caterpillar Fungus, and Chong Cao Hua. In the fungal kingdom, it belongs to the ascomycete class, a group known for its complex reproductive structures and ecological diversity. In nature, Cordyceps Militaris exhibits a unique parasitic lifestyle: its spores infect the pupae or larvae of specific insects (such as moths and butterflies). Once inside the host, the spores germinate, and the mycelium penetrates and absorbs nutrients from the insect's body, gradually replacing the host's tissues. After a period of growth and development, when environmental conditions (such as temperature, humidity, and light) are optimal, the mycelium differentiates and grows out of the host's cadaver to form a visible fruiting body—this is the "grass head" that characterizes Cordyceps Militaris.
In modern industrial production, artificial solid-state cultivation has become the mainstream method for producing Cordyceps Militaris. Unlike wild strains that rely on live insect hosts, cultivated Cordyceps Militaris uses standardized substrates such as grains (rice, wheat, corn) or processed insect-based materials. This cultivation method not only ensures consistent quality and safety but also significantly increases production efficiency, meeting the growing market demand. The fruiting bodies of artificially cultivated Cordyceps Militaris retain the core biological characteristics of their wild counterparts: they typically have a slender, upright stalk with a bright orange-yellow or reddish color, which is highly visually distinctive. The length of the fruiting body usually ranges from 3 to 8 centimeters, with a uniform thickness and a smooth surface. This unique morphological feature makes Cordyceps Militaris easily distinguishable from other cordyceps-related products in appearance.
In terms of core components, Cordyceps Militaris is rich in a variety of bioactive substances with significant health benefits. Cordycepin, one of its most distinctive components, is a nucleoside compound with unique biological activities—studies have shown that it has potential anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, and immune-regulating effects. In addition, Cordyceps Militaris contains high levels of polysaccharides (including β-1,3/1,6-D-glucan), adenosine, mannitol, and other ingredients. Among these, β-1,3/1,6-D-glucan is a key component of fungal cell walls and is widely recognized for its ability to enhance the body's immune function by activating immune cells such as macrophages and lymphocytes. Adenosine plays an important role in regulating cardiovascular function and improving blood circulation, while mannitol has moisturizing and protective effects on cells, contributing to the overall health benefits of Cordyceps Militaris.
Cordyceps Sinensis: The Industrialized Mycelium from Liquid Fermentation
Contrary to common misconceptions, the term "Cordyceps Sinensis" in the current market and industrial context does not refer to the rare wild Cordyceps sinensis (which is a protected species and subject to strict harvesting restrictions). Instead, it typically denotes the mycelium of cordyceps-related fungi produced through large-scale submerged liquid fermentation technology. Mycelium, functionally analogous to the "root and stem" network of plants, is the vegetative part of the fungus, consisting of a mass of thread-like hyphae that absorb nutrients and grow rapidly in suitable environments. The production process of Cordyceps Sinensis mycelium involves the use of bioreactors—large-scale industrial equipment that provides precise control over temperature, pH, oxygen levels, and nutrient concentrations.
The strains used for fermentation are carefully selected and validated, including Hirsutella hepiali, Paecilomyces hepiali (Cs-4), Cordyceps militaris, and other species approved by regulatory authorities for food and medicinal use. These strains are inoculated into a liquid medium (usually containing carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins, and minerals) and undergo vigorous fermentation. During the fermentation process, the mycelium proliferates exponentially, producing and accumulating a variety of active ingredients. After fermentation, the mycelium is harvested, concentrated, dried, and processed into forms such as powder, granules, or blocks, which are convenient for subsequent product development and application.
In terms of core components, Cordyceps Sinensis mycelium shares some similarities with Cordyceps Militaris, including polysaccharides, adenosine, and mannitol. These components are responsible for its immune-enhancing, anti-fatigue, and health-promoting effects. However, compared to Cordyceps Militaris, Cordyceps Sinensis mycelium generally lacks cordycepin, which is a key distinguishing feature in terms of chemical composition. The polysaccharides in Cordyceps Sinensis mycelium also have unique structural characteristics and biological activities, making them valuable ingredients in functional products. The industrialized production method of Cordyceps Sinensis mycelium offers advantages such as short production cycles, low costs, and consistent quality, making it a cost-effective alternative to wild cordyceps and a widely used raw material in the health product industry.
Applications of Cordyceps Militaris and Cordyceps Sinensis
Despite their differences, both Cordyceps Militaris and Cordyceps Sinensis are valued for their rich active ingredients and are widely used in multiple fields:
Healthcare
Both are important raw materials in the healthcare product industry. Cordyceps Militaris, with its high cordycepin and polysaccharide content, is often formulated into capsules, tablets, oral liquids, and other immune-boosting products. These products are designed to enhance the body's resistance, improve physical fitness, and alleviate fatigue, making them suitable for sub-healthy populations, the elderly, and those recovering from illness. Cordyceps Sinensis mycelium, on the other hand, is widely used in functional foods and health supplements focused on immune regulation and anti-fatigue. Its cost-effectiveness and consistent quality make it a popular choice for mass-market healthcare products.
Food & Beverage
In the food and beverage industry, Cordyceps Militaris and Cordyceps Sinensis are used as functional ingredients to develop a variety of products. For example, Cordyceps Militaris can be added to anti-fatigue beverages, energy drinks, and nutritional soups to enhance their health benefits. Its unique flavor and color also make it a popular ingredient in gourmet dishes. Cordyceps Sinensis mycelium, in powder or granule form, is often added to meal replacement powders, protein shakes, and cereal products to increase their nutritional value. It can also be used as a food additive to improve the texture and functionality of processed foods. Both ingredients are valued for their natural origin and safety, meeting the growing consumer demand for healthy and functional food products.
Cosmeceuticals
In the cosmeceutical industry, Cordyceps Militaris and Cordyceps Sinensis are used for their anti-aging, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties. Cordycepin in Cordyceps Militaris has been shown to inhibit the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reduce oxidative stress, which are key factors in skin aging. It also has anti-inflammatory effects, helping to soothe irritated skin and promote skin repair. Polysaccharides in both Cordyceps Militaris and Cordyceps Sinensis can enhance the skin's moisture retention capacity, improve skin elasticity, and reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. These ingredients are often added to facial creams, serums, masks, and other skincare products to provide anti-aging, moisturizing, and repairing benefits. In addition, their natural origin and mild properties make them suitable for sensitive skin, meeting the demand for gentle and effective skincare products.
Conclusion
Cordyceps Militaris and Cordyceps Sinensis, while sharing similar names and some common active ingredients, are distinct in terms of nature, morphology, production methods, and core components. Cordyceps Militaris is a cultivated fruiting body with a distinctive orange-yellow/red stalk and high cordycepin content, while Cordyceps Sinensis is an industrially fermented mycelium in powder, granule, or block form, lacking cordycepin but offering cost-effectiveness and large-scale production capabilities. Understanding these differences is essential for consumers to choose products that meet their needs and for industry professionals to develop high-quality, targeted products.
About Naturalin Agricultural
As a professional manufacturer of botanical extracts, Naturalin Agricultural has extensive experience and successful cases in the production, R&D, and sales of Cordyceps Militaris and Cordyceps Sinensis. Leveraging advanced production technologies and strict quality control systems, Naturalin Agricultural ensures the purity, potency, and safety of its products. To address diverse client needs, Naturalin Agricultural offers customized solutions, including product formulation, dosage form development, and private labeling services. Whether for healthcare, food & beverage, or cosmeceutical applications, Naturalin Agricultural is committed to providing high-quality cordyceps ingredients and professional support to its clients worldwide.
References
1. Zhang, Y., Li, J., & Wang, H. (2020). Chemical composition and biological activities of Cordyceps militaris: A review. Journal of Food and Drug Analysis, 28(3), 589-598.
2. Liu, X., Zhang, L., & Chen, W. (2019). Submerged liquid fermentation of Cordyceps-related fungi: A review of production, optimization, and applications. Bioresource Technology, 287, 121552.
3. Wang, Q., et al. (2021). Comparative study on the active components and antioxidant activities of Cordyceps militaris fruiting bodies and Cordyceps sinensis mycelium. Food Science and Nutrition, 9(5), 2678-2686.
4. National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China. (2015). National Food Safety Standard for Food Additives (GB 2760-2014).
5. WHO. (2018). Guidelines for the Safety Assessment of Botanicals Used in Food and Food Supplements. World Health Organization.